Health promoting physical activities
Let’s ask ourselves a question which physical activity best promotes human health. To put it simply, the human organism does not care whether we participate in a sports contest, engage in a recreational physical activity or work physically. Disregarding the emotional aspect and appeal of sports contests as well as their socializing and other effects, the main indicators important for health are known under the initialism FITT: frequency, intensity, time (duration) and type of physical strain. The type or kind of physical activity to fit these FITT indicators is not prescribed, therefore we can include among suitable physical activities any common everyday activity including walking. In other words, physical movement is important for everybody, including people who are not gifted at sports. The decisive thing is that every physical activity of higher intensity strain lasts for at least 1 hour a day for children and at least 30 minutes a day for adults. This more intensive exercise should be supplemented with activities of lower intensity strain, such as ordinary walking. Short-term high intensity of strain enhances a number of bodily functions; however, it is not necessary to maintain good health.
When judging the level of physical strain, we can in general rely on the following overview:
Low intensity exercise- Ordinary kind of work done around the house or in the garden, slow, ordinary walking, riding a bike on flat terrain, an intensive walk with a dog, sports recreation activities (volleyball, badminton, etc.).
- Harder work around the house or in the garden, quick walking, jogging, faster cycling, fitness exercise, sports recreation activities (basketball, table tennis, skating, downhill skiing, cross-country skiing, swimming shorter distances, aerobics, etc.).
- Hard manual work (forest, construction site, etc.), intensive cycling, intensive long-distance run, running with a coach, racing sports activities.
Personal intervention exercise programmes, which take into consideration everybody’s specific abilities and preconditions, are extremely important for one’s exercise routine. In order to be effective they have to meet two basic criteria:
- affect the main components of physical fitness,
- include individually acceptable and suitable physical activities.
Assuming that a school staff is composed mostly of women, a more detailed and precise manual focused on the design of personal exercise programmes can be found for example in the book Fit Programmes for Women. However, this book is rich in information and inspiring ideas also for men.
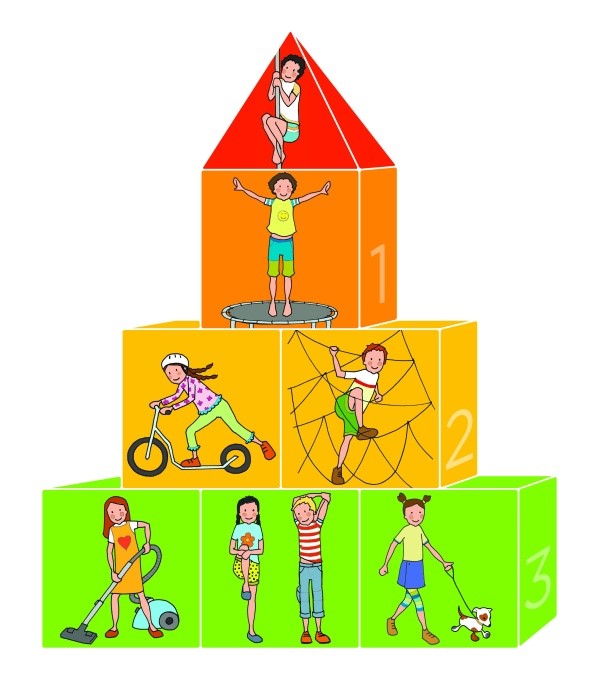
Children can understand the requirements regarding daily exercise routine and the FITT indicators for instance using the Pyramid of Physical Activities for children (Fig. 1):
- Frequency is represented through everyday completion of the whole pyramid of physical activities.
- Intensity of strain is differentiated by the division into individual floors of the pyramid. Children can understand the concept of intensity of exercise in analogy with their effort and breathlessness.
- The length of the physical activity is represented by cubes which stand for 15 - 30 minute portions of exercise. The whole pyramid thus represents approximately 45 – 90 minutes of low intensity exercise and 45 – 90 minutes of moderate or high intensity exercise.
- Types of activities are represented by various physical activities on the cubes, i.e. portions of activities.
- The pyramid is completed with a little roof which represents short-term high intensity exercise.
The pyramid corresponds to the internationally recognised requirement of at least one hour of more intensive exercise a day.