![\dots = \dfrac{8\sqrt{5}}{25} \mathrm{arctgh}\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{5}(2\operatorname{tg}\dfrac{x}{2}-1)\right] -\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot \dfrac{2\operatorname{tg}\frac{x}{2}-1}{\operatorname{tg}^2\frac{x}{2}+1} + C = \\ \phantom{\dots}= - \dfrac{1}{5} \cos x - \dfrac{2}{5} \sin x - \dfrac{8\sqrt{5}}{25} \mathrm{arctgh}\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\,(\sin x + 2 \cdot \cos x - 2)}{5 \sin x}\right] + C. \dots = \dfrac{8\sqrt{5}}{25} \mathrm{arctgh}\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{5}(2\operatorname{tg}\dfrac{x}{2}-1)\right] -\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot \dfrac{2\operatorname{tg}\frac{x}{2}-1}{\operatorname{tg}^2\frac{x}{2}+1} + C = \\ \phantom{\dots}= - \dfrac{1}{5} \cos x - \dfrac{2}{5} \sin x - \dfrac{8\sqrt{5}}{25} \mathrm{arctgh}\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\,(\sin x + 2 \cdot \cos x - 2)}{5 \sin x}\right] + C.](f.gif)
Přírodovědecká fakulta Masarykovy univerzity
Mgr. Petr Zemánek, Ph.D., Mgr. Petr Hasil, Ph.D.
II. 3. Speciální integrační metody
-
Integrály typu
tj. integrály obsahující proměnnou![\displaystyle\int f\left(x,\sqrt[\uproot{4} r_1]{x},\sqrt[\uproot{4} r_2]{x},\ldots,\sqrt[\uproot{4} r_k]{x}\right)\,\mathrm{d}x, \displaystyle\int f\left(x,\sqrt[\uproot{4} r_1]{x},\sqrt[\uproot{4} r_2]{x},\ldots,\sqrt[\uproot{4} r_k]{x}\right)\,\mathrm{d}x,](f.gif)
 pod odmocninou, kde
pod odmocninou, kde
 a
a
 jsou přirozená čísla, řešíme substitucí
jsou přirozená čísla, řešíme substitucí
 , kde
, kde
 je nejmenší společný násobek čísel
je nejmenší společný násobek čísel
 . Pomocí této substituce převedeme původní integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
. Pomocí této substituce převedeme původní integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
-
Integrály typu
![\displaystyle\int f\left(x,\sqrt[r]{ax+b}\right)\,\mathrm{d}x, \displaystyle\int f\left(x,\sqrt[r]{ax+b}\right)\,\mathrm{d}x,](f.gif)
 ,
,
 ,
,
 , řešíme substitucí
, řešíme substitucí
 . Pomocí této substituce převedeme původní integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
. Pomocí této substituce převedeme původní integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
-
Integrály typu
kde![\displaystyle\int f\left(x,\sqrt[r]{\dfrac{ax+b}{cx+d}}\right)\,\mathrm{d}x, \displaystyle\int f\left(x,\sqrt[r]{\dfrac{ax+b}{cx+d}}\right)\,\mathrm{d}x,](f.gif)
 ,
,
 ,
,
 a
a
 , řešíme substitucí
, řešíme substitucí
 . Pomocí této substituce převedeme původní integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
. Pomocí této substituce převedeme původní integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
-
Integrály typu
kde
 , tj. kvadratický polynom nemá dvojnásobný reálný kořen, řešíme pomocí tzv.
Eulerovy substituce. Existuje několik variant těchto substitucí, zde uvedeme některé z nich:
, tj. kvadratický polynom nemá dvojnásobný reálný kořen, řešíme pomocí tzv.
Eulerovy substituce. Existuje několik variant těchto substitucí, zde uvedeme některé z nich:
-
jestliže
 a kvadratický polynom má dva reálné kořeny
a kvadratický polynom má dva reálné kořeny
 , obdržíme
, obdržíme
což s použitím substituce
 převedeme na integrál z racionální lomené funkce;
převedeme na integrál z racionální lomené funkce;
-
jestliže
 a kvadratický polynom má dva reálné kořeny
a kvadratický polynom má dva reálné kořeny
 , obdržíme
, obdržíme
což s použitím substituce
 převedeme na integrál z racionální lomené funkce;
převedeme na integrál z racionální lomené funkce;
-
jestliže
 a kvadratický polynom má dva reálné kořeny
a kvadratický polynom má dva reálné kořeny
 nebo jestliže kvadratický polynom nemá reálné kořeny, můžeme použít substituci
nebo jestliže kvadratický polynom nemá reálné kořeny, můžeme použít substituci
přičemž volba konkrétních znamének je zcela libovolná, čímž obdržíme integrál z racionální lomené funkce;
-
jestliže
 , můžeme zavést substituci
, můžeme zavést substituci
s jejíž pomocí převedeme integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
-
jestliže
- Integrály typu
tedy tzv. binomický integrál, řešíme jednou z následujících substitucí
-
jestliže
 , volíme substituci
, volíme substituci
 , kde
, kde
 je společný jmenovatel
je společný jmenovatel
 a
a
 ;
;
-
jestliže
 , volíme substituci
, volíme substituci
 , kde
, kde
 je jmenovatel
je jmenovatel
 ;
;
-
jestliže
 , volíme substituci
, volíme substituci
 , kde
, kde
 je jmenovatel
je jmenovatel
 .
.
-
jestliže
- Integrály typu
kde
 řešíme pomocí substituce
řešíme pomocí substituce
-
 , jestliže
, jestliže
 je liché a
je liché a
 sudé nebo nula;
sudé nebo nula;
-
 , jestliže
, jestliže
 je liché a
je liché a
 sudé nebo nula;
sudé nebo nula;
-
 nebo
nebo
 , jestliže
, jestliže
 a
a
 jsou lichá čísla;
jsou lichá čísla;
- jestliže
 i
i
 jsou sudá čísla, případně některé z nich nula, upravíme výraz pomocí vzorců
jsou sudá čísla, případně některé z nich nula, upravíme výraz pomocí vzorců
 a
a
 . Dále pokračujeme dle získaného výsledku krokem i)-iv).
. Dále pokračujeme dle získaného výsledku krokem i)-iv).
-
- Integrály typu
řešíme pomocí substituce
- jestliže
 , volíme substituci
, volíme substituci
 ;
;
- jestliže
 , volíme substituci
, volíme substituci
 ;
;
- jestliže
 , volíme substituci
, volíme substituci
 ;
;
- jestliže nenastane ani jedna z předchozích možností, použijeme k řešení tzv.
univerzální substituci:
Potom z obrázku
získáme identity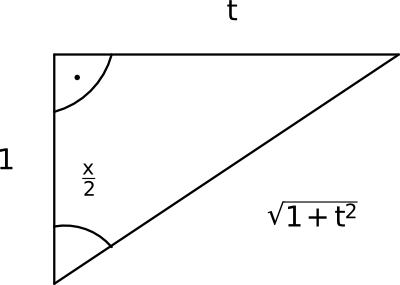

- jestliže
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
![\displaystyle\int \dfrac{x+1}{\sqrt[3]{3x+1}}\, \mathrm{d}x \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} t^{3}=3x+1 \vspace{2mm}\\ x=\dfrac{t^{3}-1}{3}\vspace{2mm}\\ 3\,\mathrm{d} x=3t^{2}\,\mathrm{d} t \end{matrix}\right\bracevert =\displaystyle\int\dfrac{\frac{t^{3}-1}{3}+1}{t}t^{2}\,\mathrm{d} t= \displaystyle\int \dfrac{x+1}{\sqrt[3]{3x+1}}\, \mathrm{d}x \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} t^{3}=3x+1 \vspace{2mm}\\ x=\dfrac{t^{3}-1}{3}\vspace{2mm}\\ 3\,\mathrm{d} x=3t^{2}\,\mathrm{d} t \end{matrix}\right\bracevert =\displaystyle\int\dfrac{\frac{t^{3}-1}{3}+1}{t}t^{2}\,\mathrm{d} t=](f.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![\displaystyle\int\dfrac{\mathrm{d}x}{\sqrt[3]{(x+2)^2}-3\sqrt[3]{x+2}-4}. \displaystyle\int\dfrac{\mathrm{d}x}{\sqrt[3]{(x+2)^2}-3\sqrt[3]{x+2}-4}.](f.gif)
![\displaystyle\int\dfrac{\mathrm{d}x}{\sqrt[3]{(x+2)^2}-3\sqrt[3]{x+2}-4} \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} t^3=x+2\\ 3t^2\,\mathrm{d} t=\mathrm{d} x \end{matrix}\right\bracevert =\displaystyle\int\dfrac{3t^2}{t^2-3t-4}\,\mathrm{d} t= \displaystyle\int\dfrac{\mathrm{d}x}{\sqrt[3]{(x+2)^2}-3\sqrt[3]{x+2}-4} \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} t^3=x+2\\ 3t^2\,\mathrm{d} t=\mathrm{d} x \end{matrix}\right\bracevert =\displaystyle\int\dfrac{3t^2}{t^2-3t-4}\,\mathrm{d} t=](f.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte


|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|

|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
Jde o binomický integrál.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
Jde o binomický integrál.
![\displaystyle\int \dfrac{(2+5x)^3}{\sqrt[4]{x^3}}\, \mathrm{d} x = \displaystyle\int x^{-\dfrac{3}{4}}(2+5x)^3 \,\mathrm{d} x \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} p=3\in\mathbb{Z} \Rightarrow x=t^4,~\mathrm{d} x = 4t^3 \,\mathrm{d} t \end{matrix}\right\bracevert = \displaystyle\int \dfrac{(2+5x)^3}{\sqrt[4]{x^3}}\, \mathrm{d} x = \displaystyle\int x^{-\dfrac{3}{4}}(2+5x)^3 \,\mathrm{d} x \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} p=3\in\mathbb{Z} \Rightarrow x=t^4,~\mathrm{d} x = 4t^3 \,\mathrm{d} t \end{matrix}\right\bracevert =](f.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
Jde o binomický integrál.

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![\displaystyle\int \dfrac{\sqrt[3]{1+\sqrt[4]{x}}}{\sqrt{x}} \,\mathrm{d} x. \displaystyle\int \dfrac{\sqrt[3]{1+\sqrt[4]{x}}}{\sqrt{x}} \,\mathrm{d} x.](f.gif)
Jde o binomický integrál.
![\displaystyle\int \dfrac{\sqrt[3]{1+\sqrt[4]{x}}}{\sqrt{x}} \,\mathrm{d} x =\displaystyle\int x^{-\frac{1}{2}}(1+x^{\frac{1}{4}})^{\frac{1}{2}} \,\mathrm{d} x \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} p=\dfrac{1}{3}\not \in\mathbb{Z}, \dfrac{m+1}{n}=2 \in \mathbb{Z}\\ \Rightarrow 1+x^{\frac{1}{4}}=t^3, x = (t^3-1)^4, \\ \mathrm{d} x = 4(t^3-1)^33t^2\, \mathrm{d} t \end{matrix}\right\bracevert = \displaystyle\int \dfrac{\sqrt[3]{1+\sqrt[4]{x}}}{\sqrt{x}} \,\mathrm{d} x =\displaystyle\int x^{-\frac{1}{2}}(1+x^{\frac{1}{4}})^{\frac{1}{2}} \,\mathrm{d} x \left\bracevert\begin{matrix} p=\dfrac{1}{3}\not \in\mathbb{Z}, \dfrac{m+1}{n}=2 \in \mathbb{Z}\\ \Rightarrow 1+x^{\frac{1}{4}}=t^3, x = (t^3-1)^4, \\ \mathrm{d} x = 4(t^3-1)^33t^2\, \mathrm{d} t \end{matrix}\right\bracevert =](f.gif)
|
|
|
|
|

|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![\displaystyle\int \sqrt{x} \,\sqrt[7]{\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x^3}}{27}-3 \right)^2}\, \mathrm{d} x. \displaystyle\int \sqrt{x} \,\sqrt[7]{\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x^3}}{27}-3 \right)^2}\, \mathrm{d} x.](f.gif)
Jde o binomický integrál.
![\displaystyle\int \sqrt{x} \sqrt[7]{\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x^3}}{27}-3\right)^2} \mathrm{d} x =\displaystyle\int x^{\frac{1}{2}} \left(-3+\dfrac{1}{27}x^{\frac{3}{2}}\right)^{\frac{2}{7}} \mathrm{d} x \displaystyle\int \sqrt{x} \sqrt[7]{\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x^3}}{27}-3\right)^2} \mathrm{d} x =\displaystyle\int x^{\frac{1}{2}} \left(-3+\dfrac{1}{27}x^{\frac{3}{2}}\right)^{\frac{2}{7}} \mathrm{d} x](f.gif)
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
Jde o binomický integrál.
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce převeďte binomický integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
![]()
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce převeďte binomický integrál na integrál z racionální lomené funkce.
![]()
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|

|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|

|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
Tento příklad je jedním z mála příkladů, které lze řešit jiným způsobem než univerzální substitucí
![]() , ale právě využití této substituce je nejvýhodnější. (Porovnejte s Příkladem 391.)
, ale právě využití této substituce je nejvýhodnější. (Porovnejte s Příkladem 391.)

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()
Tento příklad je možné řešit substitucí
![]() a následně substitucí
a následně substitucí
![]() . Výhodnější je ale následující způsob.
. Výhodnější je ale následující způsob.

|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce vypočtěte
![]()

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Pomocí vhodné substituce převeďte daný integrál na integrál racionální lomené funkce.
![]()

|
|

|
|

|
Tisková verze
ÚMS, Přírodovědecká fakulta, Masarykova univerzita |
Návrat na úvodní stránku webu, přístupnost |
| Servisní středisko pro e-learning na MU
| Fakulta informatiky Masarykovy univerzity, 2012
Technické řešení této výukové pomůcky je spolufinancováno Evropským sociálním fondem a státním rozpočtem České republiky.


