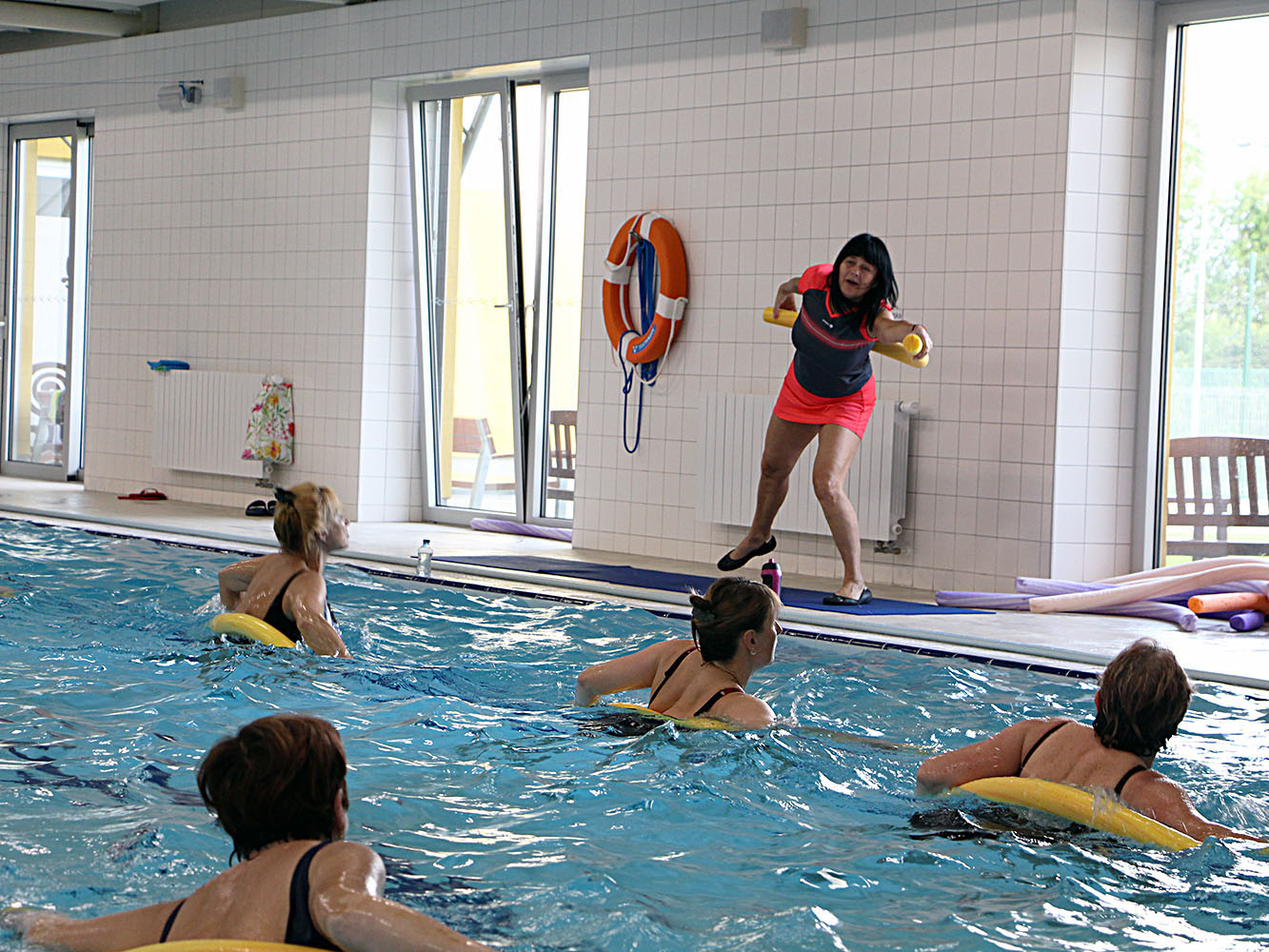Physical activities in water environments
A water environment brings along new conditions for physical activities. Thanks to the unique physical properties of water the musculoskeletal system is relieved, the speed lowers and exercises and movement change because of the water resistance. Therefore these physical activities are suitable also for disabled people. Aquatic activities are beneficial for the whole organism: regarding health-oriented fitness, musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, thermoregulation as well as movement coordination, endurance, spatial orientation, flexibility, psyche, etc. Right above the water surface the air is saturated with water vapour and contains only a few dust particles, which is beneficial for the upper air passages and therefore suitable for people with some respiratory disorders.
A water environment is used for sports, recreational, physiotherapeutical or relaxation purposes.
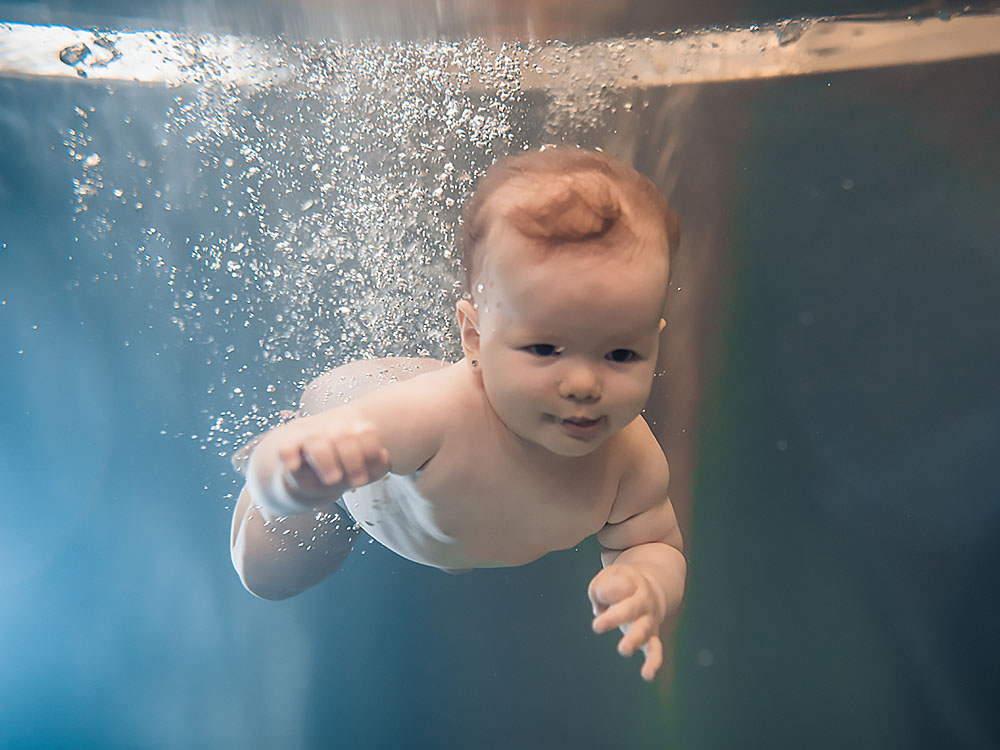
Swimming and games for babies and toddlers
The views of experts and laymen regarding swimming for babies and toddlers differ. Among the frequently cited positive aspects of swimming at this age we can mention improvements to psychomotor development, to the fine and gross motor skills, appropriate strain on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and their enhanced function, strengthening of all components of the musculoskeletal system without a strain being put on joints, development of strength, endurance and coordination, improved body defences and resistance to cold, lowered fear of water and, last but not least, positive effects on social development (tight bond with parents, movement in a group).
Children who attend swimming courses sleep better and eat better. Among the negatives we can name potential development of allergies or asthma as a reaction to chemical substances dissolved in the water, skin and digestion problems caused by the polluted water, inflammation of the air passages as a consequence of poor drying after swimming or the cold water in the pool (should be 28°C).
Swimming with babies is usually done in bathtubs and pools (best without chlorinated water), whereas toddler classes take place in pools. The duration of a lesson is 30 minutes at most.
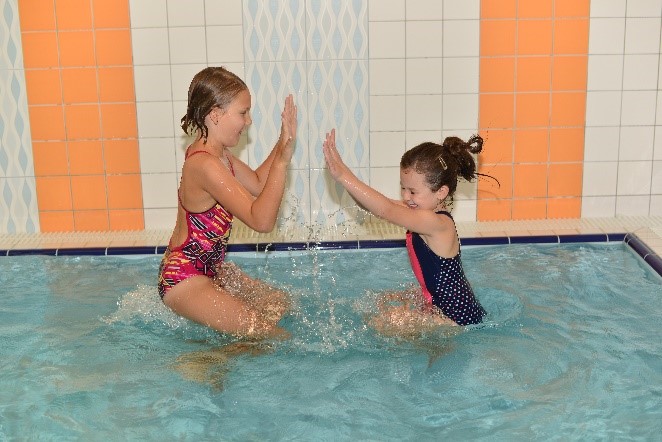
Swimming and games for pre-school and school children
For pre-school and school children physical activities in water environments are associated with games. Games are usually connected to motivation (fairy-tales – e.g. Moving water tales (not only) for pre-schoolers, poems and imagination) and are aimed at training and development of basic swimming skills and strokes. Depending on the age and skills achieved, children are placed into ability groups. A lesson is 30 – 60 minutes long.
Examples of games and activities:
- Games to get acquainted with water - games aimed at getting rid of the fear of water and submerging the head (e.g. playing tag – individual children, pairs, threes, groups; diving games; splashing games; games using equipment, etc.)
- Games for getting around in water – games for the development of spatial orientation above and under water (e.g. hunting for objects; identifying numbers underwater; swimming under something; jumps and falls, etc.)
- Games for breathing – games aimed at forming basic habits of directed breathing for swimmers
- Games for floating – the target skill is to put and maintain the body in the horizontal position on the water surface (e.g. a little star with a swimming board under the body; a little star; a mushroom; sending "little boats", etc.)
- Elements of swimming and coordination – separate practice of lower and upper limb movements and subsequent coordinated practice of a particular stroke
Video chapters
- Beginning
- Games for getting acquainted with water
- Elements of swimming and coordination
Swimming and aquafitness in adulthood and old age
In adulthood physical activities focused on fitness or health-oriented swimming and aquafitness are preferred.
Fitness-oriented swimming counts as a cyclic aerobic activity which can be done by anybody regardless of sex, age or fitness. It is also suitable for physically challenged people (e.g. for people with problems of the musculoskeletal system, obesity, etc.).
The basic position is lying on the stomach or on the back (depending on the chosen stroke), which puts a balanced strain on the whole organism, in a position favourable for the cardiovascular and respiratory system. Thanks to the properties of the water environment aquatic activities lack hitting and shocks and there is little strain put on the lower limb joints. It is said that when swimming a person uses twice to five times more energy and strength than on land and burns 1 800 – 2 000 kJ / hour.
Back stroke is considered the healthiest stroke. The swimmer is in a horizontal position on his back, the head in line with the torso. Considering the fact that the face is directed upwards and there is no problem regarding breathing, it is often the first stroke taught to children. However, in fitness swimming it is not widely used.
The opposite is true. The most frequently used stroke is the breast stroke. It is the slowest stroke. The swimmer lies on his stomach. Demanding coordination of the movement of the limbs and breathing out under water makes this stroke difficult for many swimmers. In swimming complexes we can usually see people doing breast stroke without submerging their heads and breathing into the water, which in the long run negatively affects the neck and shoulders (head bent back, fatigue, pain).
Crawl is the fastest stroke done in a floating position on the stomach. The head is in line with the torso, and the limbs move fluently. The biggest problem is breathing into the water, which must be practised. Crawl is the second most frequently used stroke in fitness swimming. The second fastest is the butterfly stroke. The basic swimming position is on stomach, and the wavy movement engages the whole body. It is a demanding swimming stroke in terms of coordination and physical fitness, which is why it is not frequently used in ordinary fitness swimming.
Aquafitness encompasses different forms of movement in the water. One of the many kinds of group exercises done in water and accompanied by music is aqua aerobics. It is a fitness activity focused on the cardiovascular, respiratory and musculoskeletal system. People exercise in different depths (shallow water – reaching the chest, transition – reaching the shoulders, deep – no contact with the bottom, using floating equipment), with or without training equipment (e.g. dumb-bells, pool noodles, gloves, aqua belts, aqua steps, etc.). The body is often in the upright position, and modified steps, running, jumping and variations are used.
Video chapters
- Beginning
- Aqua aerobic
- Fitness swimming