Other life-threatening conditions
Stroke
- = a cerebrovascular accident = CVA
Definition of a stroke
An urgent condition caused by a sudden disruption of the blood perfusion of the brain, which may lead to irreversible brain tissue damage.
- a sudden change in the patient’s condition
- the risk factors of a stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, etc.
- a stroke does not affect only older patients; it may happen to a young person, too
- the two types of a stroke:
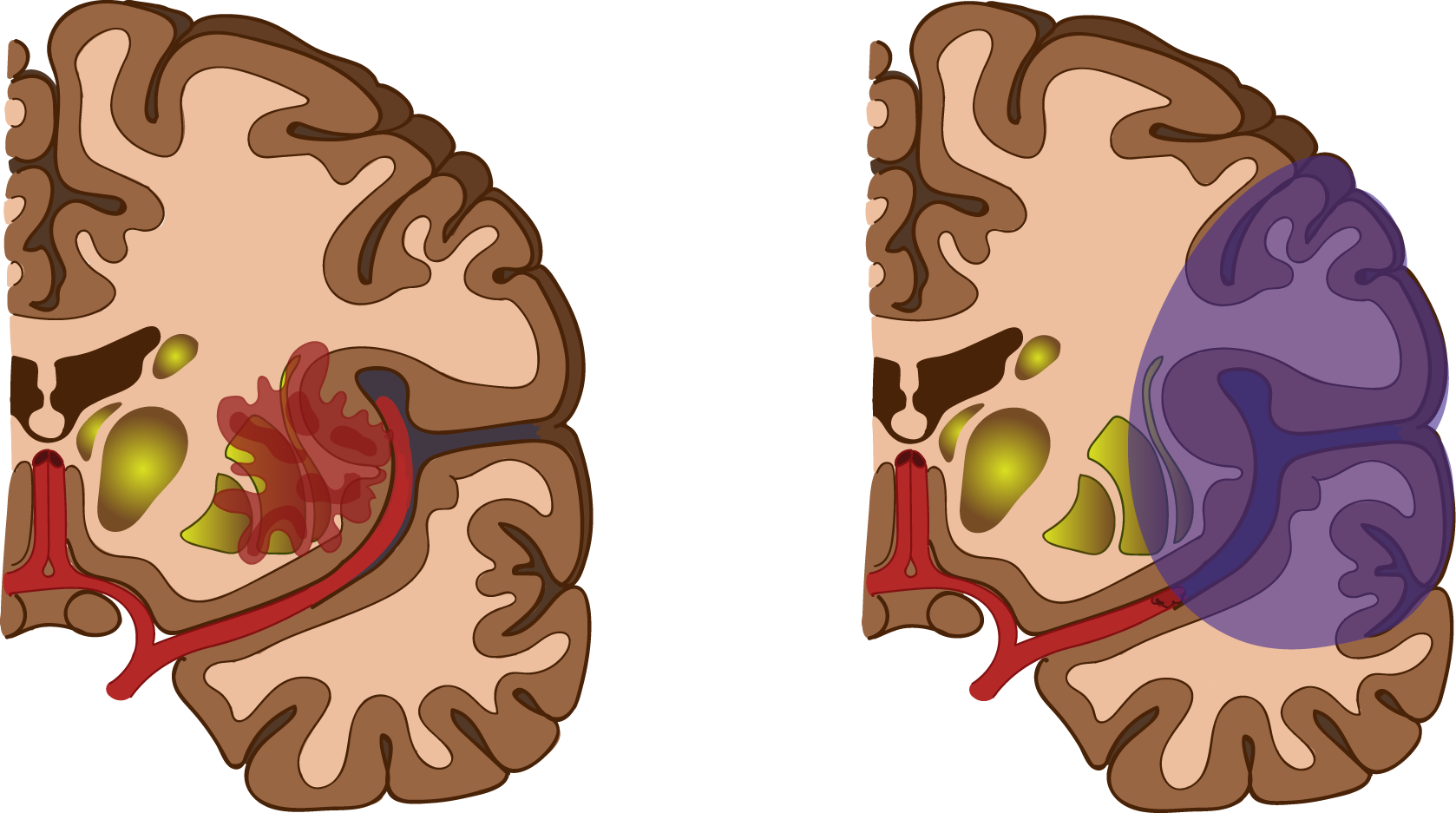
- ischemic - caused by a clot in a blood vessel that blocks the flow of blood to the brain (80 % of cases)
- hemorrhagic - caused by bleeding from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain (20 % of cases)
Signs and symptoms
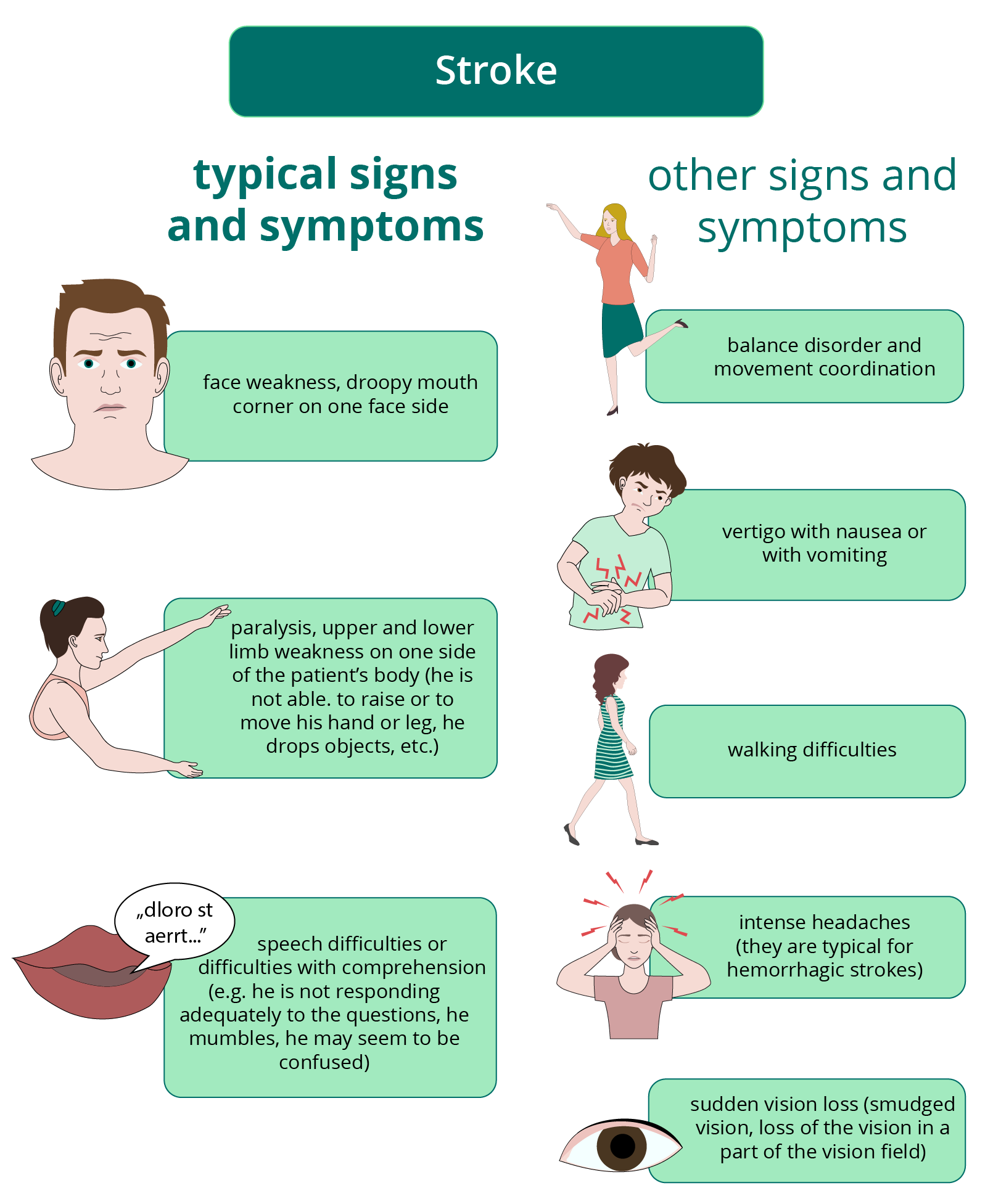
- the stroke can show any of the symptoms stated above; it is enough if only one of them is present
First Aid
- use SSS ABC approach
- if you suspect a stroke, use the FAST acronym:
- F (face) - focus on the patient’s face, ask him to smile - Does one side of the face droop or is it numb? Is the person's smile uneven or lopsided?
- A (arms) - raise the patient’s arms in front of him, ask him to close their eyes - Is one arm weak or numb? Does one arm drift downward after closing the eyes?
- S (speech) - ask the patient simple questions, e.g. what his name is - Do he answer adequately? Can you understand what he is saying? Is the person unable to speak?
- T (time) - if the person shows any of these symptoms, even if the symptoms go away, call EMS immediately
- communicate with the patient, try to calm him down
- observe the patient and check him regularly until the EMS arrives
- if the patient is unresponsive, open the airway and check the breathing
- YES, the patient is breathing normally - check the patient regularly; if he stops breathing, start providing CPR
- NO, the patient is not breathing normally - start providing CPR
- report any change in the patient’s condition to the EMS
Complications of a stroke
- disorder of the consciousness - place the patient in a safe position (sit them down, if possible, or lay them on the ground) and check them regularly
- the patient loses consciousness, becomes unresponsive, after opening the airway is/is not breathing normally - see above
In which patients would you suspect a stroke?
| an 80-year-old woman; gradually increasing speech difficulties, especially with pronunciation; however, the nurse from the nursing home claims this has been going on for several months now, along with the limited movement of the limbs | |
| a 50-year-old man; responsive, sitting in a vehicle that suddenly drove off the road into the ditch at a low speed; when asked, his answers do not make any sense, one corner of his mouth droops down | |
| a 25-year-old woman; a sudden loss of vision in a part of her vision field and a weakness of her upper limb - she is trying to grab her mobile phone from the table, but it keeps falling from her grasp |
Take home message:
- The stroke may show various signs and symptoms, typically an asymmetry of the face (e.g. a droopy mouth corner), limb weakness and problems with speech or understanding, as the FAST acronym reminds us.
- If you suspect a stroke, call EMS as soon as possible.