Approach to the unresponsive patient
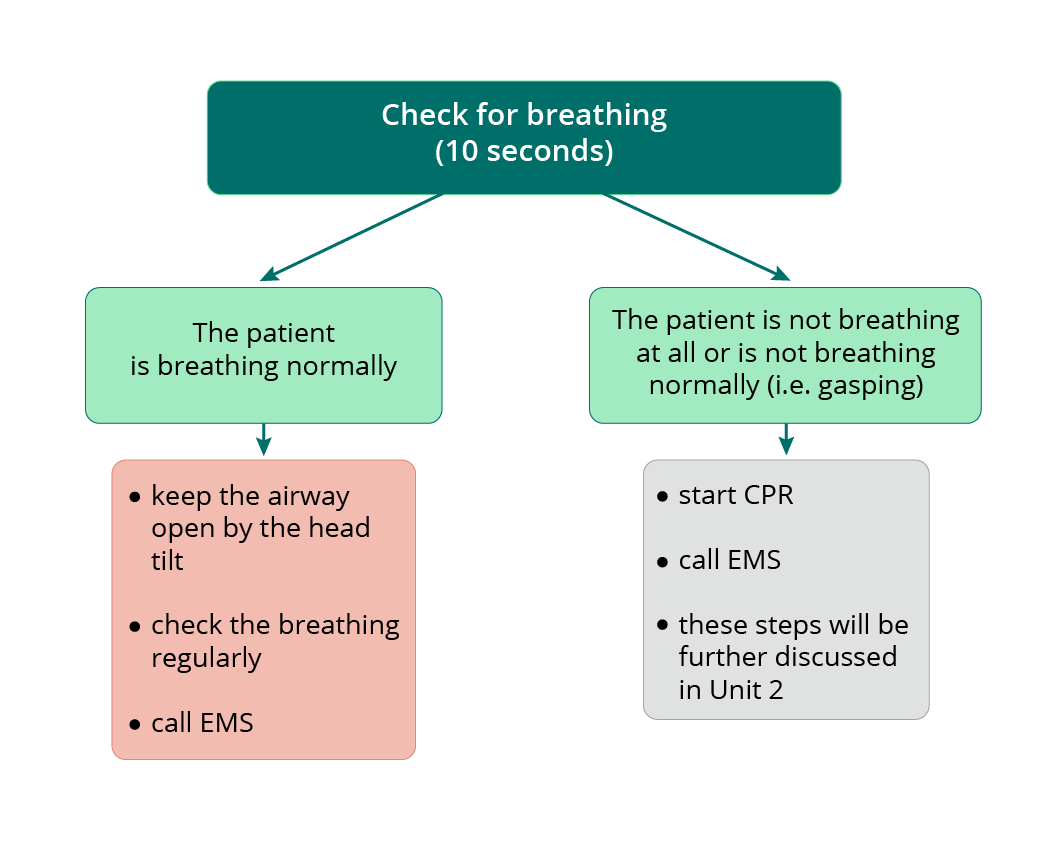
Checking for the breathing
- we check the patient's breathing for no more than 10 seconds
How to check the patient's breathing?
- keep the patient's head in the tilted position so that the airway is still open
- place your ear above the patient's mouth, look at the patient's chest
- check the patient's breathing for no more than 10 seconds by:
- look - look if the patient's chest is moving (when the patient wears several layers of clothing, remove some pieces of it to make the chest movement more visible)
- listen - listen to the sounds of the exhaled airflow
- feel - feel the exhaled airflow on your cheek
What does it mean that the patient is breathing normally?
- you are sure that patient is breathing
- you can see the chest movements, hear and feel the exhaled airflow
- you are sure that the patient is not gasping (see below)
If you have any doubt whether the patient's breathing is normal, act as if he/she is not breathing normally and start CPR.
How is gasping defined? What does it look like?
- = agonal breathing
- the patient gasps for breath
- it frequently occurs in cases of cardiac arrest (more than 40 % of all cases)
- it is the response of CNS to the reduced oxygen supplies
- irregular, barely noticeable, noisy breathing
- the patient may resemble a fish which is out of water and gasps for breath
- there are no chest movements
- the intervals between the breaths gradually lengthen until gasping stops completely
Gasping is not considered normal breathing. The gas exchange in the lungs is ineffective, so you have to start CPR.
How to proceed if you have a suspicion that the patient's spine is injured?
When you take care of an unresponsive patient, it is always your absolute priority to control the patient's vital signs.
- it includes the airway management, check for breathing and eventually starting CPR
- if you have a suspicion of a spinal injury by the patient, try to avoid excessive rotation and tilting the head to the side, however, always follow the algorithm SSS ABC